Blog Article

This research project, in collaboration with West Midlands Combined Authority (WMCA), aims to develop smarter traffic monitoring technology to enable the authority to gather important traffic flow and emissions data.
Researchers
- Alan Dolhasz
- Mattia Colombo
Research background
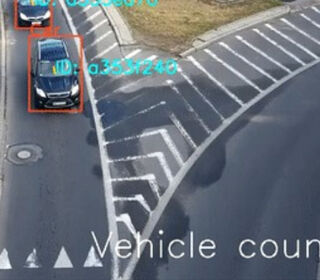
The DMT Lab was approached by WMCA to research and develop a low-cost vision-based system for detection, classification and tracking of vehicles in video streams from traffic monitoring systems. After a pilot project, WMCA funded the development of a first working prototype, to be tested on the West Midlands road network. This project is also the result of ongoing collaboration between BCU, WMCA and BCC in applying data science and machine learning to traffic management.
Research aims
The aim of this research is to develop computer-vision-based techniques for traffic monitoring, to compliment and eventually replace legacy traffic monitoring techniques. This will allow the extraction of rich traffic pattern data, which can then be used to predict and mitigate congestion, detect various traffic-related incidents and support related analytics. Additionally, the project aims to develop solutions that are efficient, affordable and compatible with existing monitoring systems.
Research methods
The project is developing computer vision algorithms using state-of-the-art deep learning models. The goal of these algorithms is to accurately detect, classify and track instances of vehicles in the view of a given camera. These algorithms will first be evaluated against annotated traffic count videos provided by WMCA and BCC in order to minimise the error between the output of the proposed system and ground truth traffic counts. The final stage of the project focuses on deployment and integration of the proposed system on WMCAs traffic monitoring network.
Projected outcomes
- Accurate and efficient algorithms for extraction of traffic metrics from video data
- A long-term reduction in costs of obtaining accurate traffic flow data for the local council, leading to decreased reliance on commercial data providers
- Improving the cost-efficiency and utilisation of new traffic monitoring cameras being installed across the Midlands
- Application of these techniques to other smart-city-related data collection, such as emissions or lane occupancy.